What is Cloud Computing?
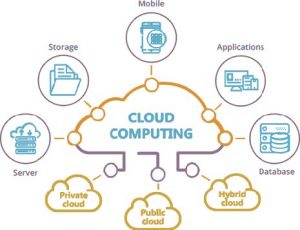
With expanding internet use, the internet of things (IoT), and the big data applications, we have seen the term cloud computing everywhere. In its most basic form, Cloud computing entails storing and accessing data and programs over the internet rather than on your computer’s hard drive. Cloud-based storage allows you to save files to a remote database rather than storing them on a private hard drive or local storage device. As long as an electrical gadget has internet access, it has access to the data and the software programs needed to run it. It can access the technology services, such as computer power, storage, and databases, from the cloud provider on the necessary basis, rather than purchasing, operating and maintaining physical data centers and servers. Also, cloud computing gives a benefit to process massive data in the cloud. That provides high speed and performance in processing huge data without having high computer equipment.
For many reasons including cost savings, productivity increase, and speed, performance, and safety, cloud computing is a popular alternative for individuals and companies. Especially in the finance sector, cloud computing is prevalent and important. Gill (2011) stated that “The cloud application wave has reached the finance organization where it promises the same impact—lower cost, easier collaboration, and faster innovation.”
Top benefits of cloud computing
Cost
Including the creation and running of data centers, cloud computing reduces the expense of capital for hardware and software acquisition which are server racks, powering and cooling 24/7 electricity, and IT infrastructure management experts.
Speed
Most cloud computing services are delivered with self-service and available on-demand, so even many computer resources can be offered in minutes, usually with few clicks.
Global Scale
The ability to scale elastically includes the advantages of cloud computing services. In the cloud, that implies that you deliver the right number of IT resources—for example, more or less computer power, storage, bandwidth—from the right position when necessary.
Productivity
There are usually many “racking and stacking” on-site datacenters — hardware setup, software patching, and other time-consuming IT management tasks. The need for many of these functions is removed by cloud computing so that IT teams have time to reach more relevant business objectives.
Performance
The world’s largest cloud service providers run on a secure data center network that is periodically updated to a state-of-the-art computing technology generation. There are a number of advantages over a single corporate data center, including decreased network latency and increased scale savings.
Reliablity
Cloud services simplify and reduce costs in terms of data back-up, disaster recuperation, and business continuity because data may be viewed on many redundant sites on the network of the cloud provider.
Security
Many cloud services offer a large number of policies, technologies, and controls to improve security position overall and to help prevent possible threats to data, applications, and networks.
Source
What is cloud computing. (n.d.). Amazon Web Services, Inc. https://aws.amazon.com/what-is-cloud-computing/
Gill, R. (2011). Why cloud computing matters to finance. Strategic Finance, 92(7), 43+.
