Supply chain
A supply chain is the network of all the individuals, organizations, resources, activities and technology involved in the creation and sale of a product. A supply chain encompasses everything from the delivery of source materials from the supplier to the manufacturer through to its eventual delivery to the end user. The supply chain segment involved with getting the finished product from the manufacturer to the consumer is known as the distribution channel.
Steps in the supply chain
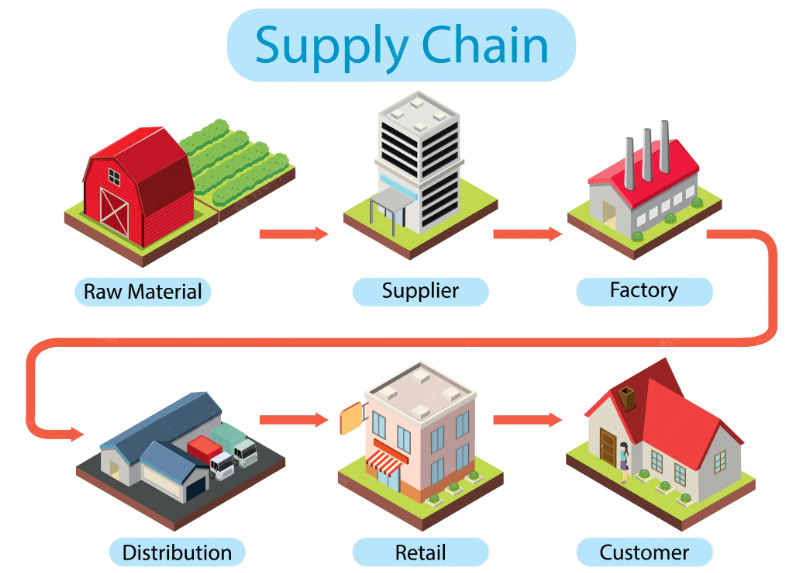
The fundamental steps of a supply chain in order are as follows:
- Sourcing raw materials.
- Refining those materials into basic parts.
- Combining those basic parts to create a product.
- Order fulfillment/Sales.
- Product delivery.
- Customer support and return services.
The amount of time it takes any one of these processes from start to completion is known as lead time. Supply chains are managed by supply chain managers, who monitor lead time and coordinate the processes in each step to maximize customer satisfaction.
Supply chains can be contrasted against value chains — they contribute to the end product in different ways. Supply chains aim to meet customer demands. Value chains seek to add value to a product on top of its inherent value. The purpose of the value chain is to give the company a competitive advantage in the industry. Supply chain management and value chain management are two slightly different perspectives on the same basic process and work in tandem to meet two slightly different definitions of “demand.”
Supply chain management
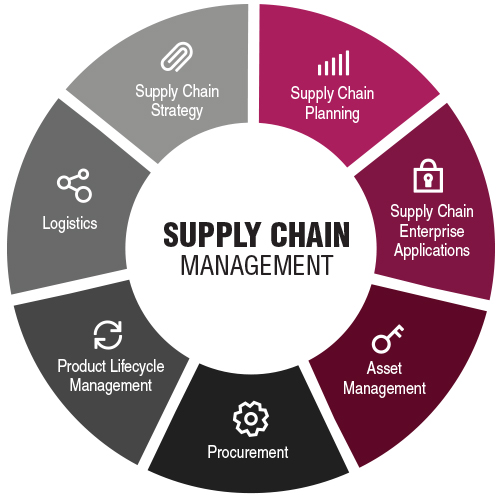
Supply chain management (SCM) is the oversight of materials, information and finances as they move in a process from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer and then to the consumer. The three main flows of the supply chain are the product flow, the information flow and the finances flow. These occur across three main stages: strategy, planning and operation. SCM involves coordinating and integrating these flows both within and among companies.
Supply chain models
There have been several different efforts to employ blockchains in supply chain management.
- Shipping industry — Incumbent shipping companies and startups have begun to leverage blockchain technology to facilitate the emergence of a blockchain-based platform ecosystem that would create value across the global shipping supply chains.
- Precious commodities mining — Blockchain technology has been used for tracking the origins of gemstones and other precious commodities. In 2016, The Wall Street Journal reported that the blockchain technology company Everledger was partnering with IBM’s blockchain-based tracking service to trace the origin of diamonds to ensure that they were ethically mined. As of 2019, the Diamond Trading Company (DTC) has been involved in building a diamond trading supply chain product called Tracr.
- Food supply — As of 2018, Walmart and IBM were running a trial to use a blockchain-backed system for supply chain monitoring for lettuce and spinach — all nodes of the blockchain were administered by Walmart and were located on the IBM cloud.
- Fashion industry — There is an opaque relationship between brands, distributors, and customers in the fashion industry, which will prevent the sustainable and stable development of the fashion industry. Blockchain makes up for this shortcoming and makes information transparent, solving the difficulty of sustainable development of the industry.